Fiber Optic Fundamentals: A Beginner’s Guide
As demand for higher bandwidth and richer content explodes, fiber optic networks may soon become a business’ most valuable asset. Fiber optic cables, also known as optical cords, transmit data in the form of light by using thin strains of glass. On the other hand, traditional cables, such as those made from copper, rely on electricity to carry data from one point to another. However, the bottom line is that light as a data transmission medium can carry more data, quicker, and over longer distances than electricity.
But how do fiber optic networks work?
Well, the answer lies in the fiber optic cable’s design.
An Introduction to Fiber Optics
In the American west, Apache tribes used to communicate over vast distances with smoke signals. The signaler started a fire, usually from an elevated position, made up of damp grass. The fire would then produce a column of smoke. And depending on its location and intensity, the smoke would convey a message. Sometimes the message meant all was well, but other times it signified danger.
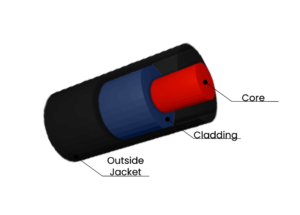
Fiber optic cables similarly convey information. But instead of smoke, fiber cables use light to transmit encoded data over certain distances. Fiber optic cables contain a glass core cladding, and buffer coating. The cladding is a reflective material that wraps around the glass core, while the buffer coating is the protective outermost layer.
However, all the action takes place inside the glass core. Here, in a diameter not larger than a human hair, the beauty of fiber optic cables plays out in a delicate dance of light known as Total Internal Reflection (TIR).
Reflection vs. Refraction: Not Something to Make Light of
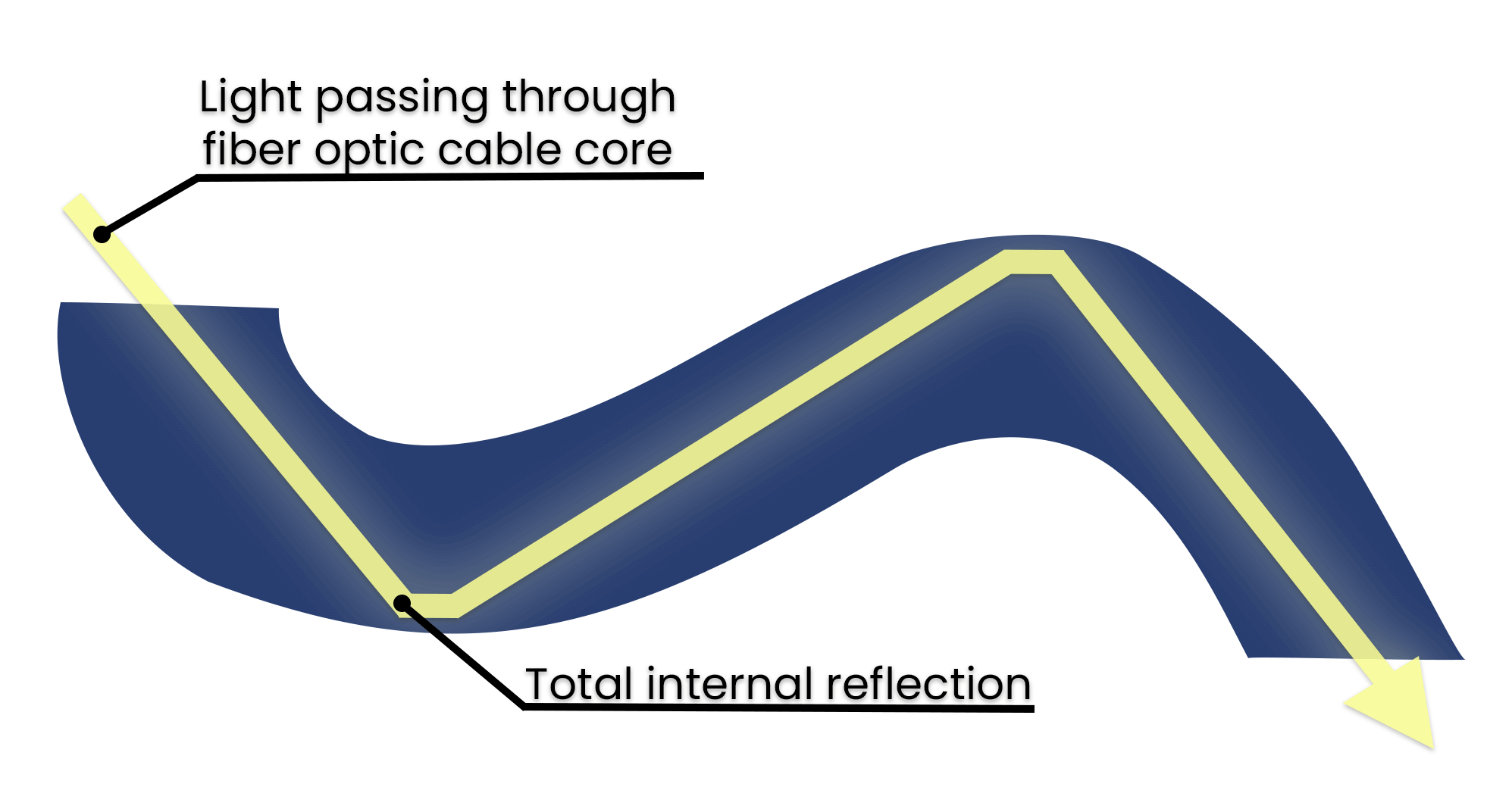
Whenever light hits a surface it can either be reflected (reflection) or pass through (refraction). For instance, have you ever been swimming, dove underwater, and looked up at the sky from under the water? Did you notice that the surface of the water looked like a mirror? That effect is due to total internal reflection.

Fiber cables utilize this property of light within their internal structure. Fiber optic equipment shoots encoded data in the form of light down the glass core at a precise angle to ensure complete reflection. The physics behind this bizarre property of light is proven by the formula of Snell’s Law, or the law of refraction.
But unless you’re working on your PhD, just remember that fiber optic cables transmit data by making light bounce around the fiber core (reflection). If the angle is off by a fraction, the light will leak out of the glass core (refraction).
What happens when light is refracted?
Luckily, the cladding is designed to decrease refraction by using special chemicals like boron and germanium to help keep light confined to the glass core.
It’s undeniable that our modern world demands the rapid transfer of massive amounts of information. A few years ago, metal cables made of copper transferred data. But now, fiber optics have replaced traditional cables as a better means of communication. Understanding how fiber optic cables work helped me to see how they could smoothly transmit data over continents and oceans alike.
The Benefits of Fiber Optic Cables
The wide-spread use of fiber optic cables around the globe is due to its unsurpassed advantages: longer distances with less attenuation, higher bandwidth, and faster speed. Yet optical cables are a relatively new technology, which means many businesses may not be aware of the benefits. Some businesses might be concerned that installing fiber optic networks is more expensive than employing traditional copper cables. For this reason, many businesses don’t see a need for fiber connectivity. However, the benefits of optical cables listed below will offset any cost of installation.
- Longer Distances: The 328ft limit on copper wires cripples high bandwidth data transmission, requiring additional equipment to extend the signal. Fiber optics are also capable of providing low power loss, which means that signals travel farther with no problem.
- Secure Communication: Worried about someone “tapping into” your fiber optic networks and stealing data? Well, any attempt to penetrate the glass core will cause light to leak out and show noticeable degradation. Also, optical cables don’t radiate electromagnetic energy so emissions cannot be intercepted. For these reasons, fiber cables are considered among the most secure form of communication.
- Higher Bandwidth: No other cable offers the bandwidth that fiber optics offer. The volume of data transmitted per unit of time is higher than traditional copper cables. In addition, bandwidth speed doesn’t decrease as demand on the network increases. Uninterrupted internet speed is excellent for businesses that rely on tasks such as web conferencing, file sharing, or cloud applications.
- Faster Speed: Fiber optic cables can transmit data at a higher volume than traditional cables, such as those made of copper. The diameter of the glass core is no larger than a strain of human hair. Yet it can support bandwidth speeds above 10 gigabits. The same speed would require larger diameter metal cables aggregated together to reach the speeds of one fiber strand.
Businesses should consider fiber optic networks because of their efficiency and high transmission capacity. Propelled by increasing demand for faster, more secure, and robust bandwidth, fiber optic cables are more common in modern society. Only optical cables can cater to future demand for higher-quality services.
The Megladon Difference
Megladon Manufacturing, located in Austin, Texas, has spent over 20 years developing and perfecting a full spectrum of fiber optic products. We also offer a larger array of customizable options at competitive prices that you won’t find anywhere else on the planet. If you would like to speak to one of our specialists about your networking needs, contact us at (512) 491-0006.

